You're about to launch a new product, but you aren't sure how much to produce or how much to charge. Price it too high or make too much of it, and you could be left with unsold stock. If you price too low or don't make enough, you'll lose potential profit. Everything depends on the demand for the product — how much customers will buy at what price. That's why the law of supply and demand is so relevant to business decisions. It predicts the relationship between supply, demand and pricing. Understanding the law of supply and demand can help businesses meet customer demand while maintaining healthy profits and minimising excess stock.
What Is the Law of Supply and Demand?
The law of supply and demand is the theory that prices are determined by the relationship between supply and demand. If the supply of a good or service outstrips the demand for it, prices will fall. If demand exceeds supply, prices will rise.
The law of supply and demand is based on two other economic laws: the law of supply and the law of demand. The law of supply says that when prices rise, companies see more profit potential and increase the supply of goods and services. The law of demand states that as prices rise, customers buy less.
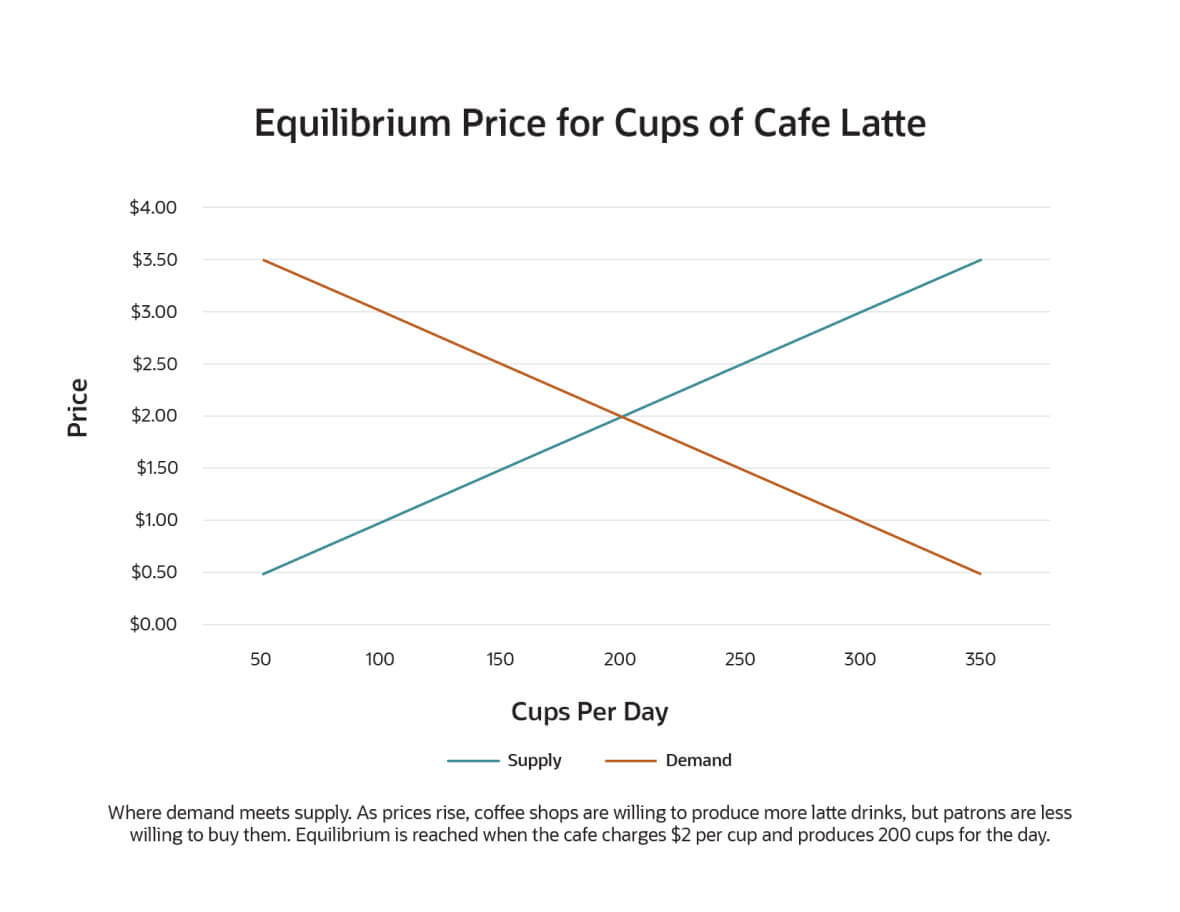
Theoretically, a free market will move toward an equilibrium quantity and price where supply and demand intersect. At that point, supply exactly matches the demand — suppliers produce just enough of a good or service, at the right price, to satisfy everyone's demands.
Key Takeaways
- The law of supply and demand predicts that if the supply of goods or services outstrips demand, prices will fall. If demand exceeds supply, prices will rise.
- In a free market, the equilibrium price is the price at which the supply exactly matches the demand.
- Understanding the law of supply and demand helps businesses determine how to set prices and fulfil customer demand while minimising excess inventory.
Law of Supply and Demand Explained
The law of supply and demand describes how the relationship between supply and demand affects prices. If a supplier wants more money than the customer is willing to pay, items will most likely stay on the shelf. If the price is set too low, customers will be eager to buy the items, but each item will be less profitable. The law of supply and demand is based on the interaction between two separate economic laws: the law of supply and the law of demand. Here's how they work.
The Law of Supply.
The law of supply predicts a positive relationship between pricing and supply. As prices of goods or services rise, suppliers increase the amount they produce — as long as the revenue generated by each additional unit they produce is greater than the cost of producing it. Seeing a greater potential for profits, new suppliers may also enter the market. For example, prices of lithium and other metals used in batteries have soared as sales of electric vehicles have increased. That has encouraged mining companies to explore new sources of lithium and expand production at existing mines in order to increase the supply and generate higher profits.
The law of supply can also operate on a local scale. Let's say a well-known musician is coming to town. Anticipating a huge demand for tickets, promoters aim to maximise the supply by booking the biggest venue possible and offering as many tickets as they can, at high prices. As the supply of tickets runs out, the price of secondhand tickets rises — and so does the supply — as casual fans who bought tickets at the list price see the opportunity to resell them at a higher price. As a result, they enter the market as new suppliers.
The Law of Demand.
The law of demand says that rising prices reduce demand. So as prices rise, customers buy less. That's particularly true if they can substitute cheaper goods. When the famous musician comes to town, not everyone may be able to afford a ticket even if they'd like to go. So, if the theater sets prices too high, fewer people will decide it's a worthwhile purchase, and the show organisers will be left with empty seats. Fans who want to resell their tickets may need to lower their asking price. Some people may decide to see another artist instead, if those tickets are cheaper.
The Law of Supply and Demand.
The price where supply and demand meet is known as the equilibrium price. At that price point, suppliers produce just enough of a good or service to satisfy demand, and everyone who wants to purchase the product can do so. In practice, of course, balancing supply and demand is more complex. As supply and demand fluctuate, the equilibrium price can vary over time. Furthermore, the law of supply and demand assumes that all other factors that can affect pricing remain constant. In reality, that's often not the case. For example, fluctuating production costs or supply chain problems can have a big impact on pricing.
Why Is the Law of Supply and Demand Important?
Business success in any competitive market depends on accurately assessing supply and demand. Every company that launches a new product needs to determine how much of the product to make and how much to charge. A business that manufactures too much of a product or sets prices higher than customers will pay can easily find itself left with products that don't sell and become dead stock. On the other hand, understocking or setting prices too low reduces profits and can drive away customers who can't wait for backorders to be fulfilled. Demand forecasting can help businesses determine the optimal supply level and find the equilibrium price — the price at which the supply just meets customer demand.
4 Basic Laws of Supply and Demand
The law of supply and demand predicts four ways that changes in either demand or supply will drive changes in pricing:
-
Prices fall when supply increases and demand remains constant.
If supply increases without a change in demand, a surplus usually occurs. This can happen for many reasons, including surges in productivity. To move excess stock, especially if there's a pending expiration date, suppliers tend to lower prices to try to boost demand.
-
Prices fall when demand decreases and supply remains constant.
A surplus can also occur when customers want less of a good or service, even without a change in supply. The effect is the same: lower prices.
-
Prices rise when supply decreases and demand remains constant.
If supply drops, shortages occur. In that situation, customers are often willing to pay higher prices to get the goods and services they want. Supply constraints can occur for many reasons, including supply chain problems. If the problem is temporary, prices tend to return to their baseline once supply is restored.
-
Prices rise when demand increases and supply remains constant.
A shortage can occur if the demand for a product increases but the supply doesn't — or if demand increases faster than production can ramp up. When supply eventually catches up with demand, prices tend to stabilise.
| Supply | Demand | Inventory Level | Price Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increases | Remains constant | Surplus | Lower |
| Remains constant | Decreases | Surplus | Lower |
| Decreases | Remains constant | Shortage | Higher |
| Remains constant | Increases | Shortage | Higher |
Demand Curve
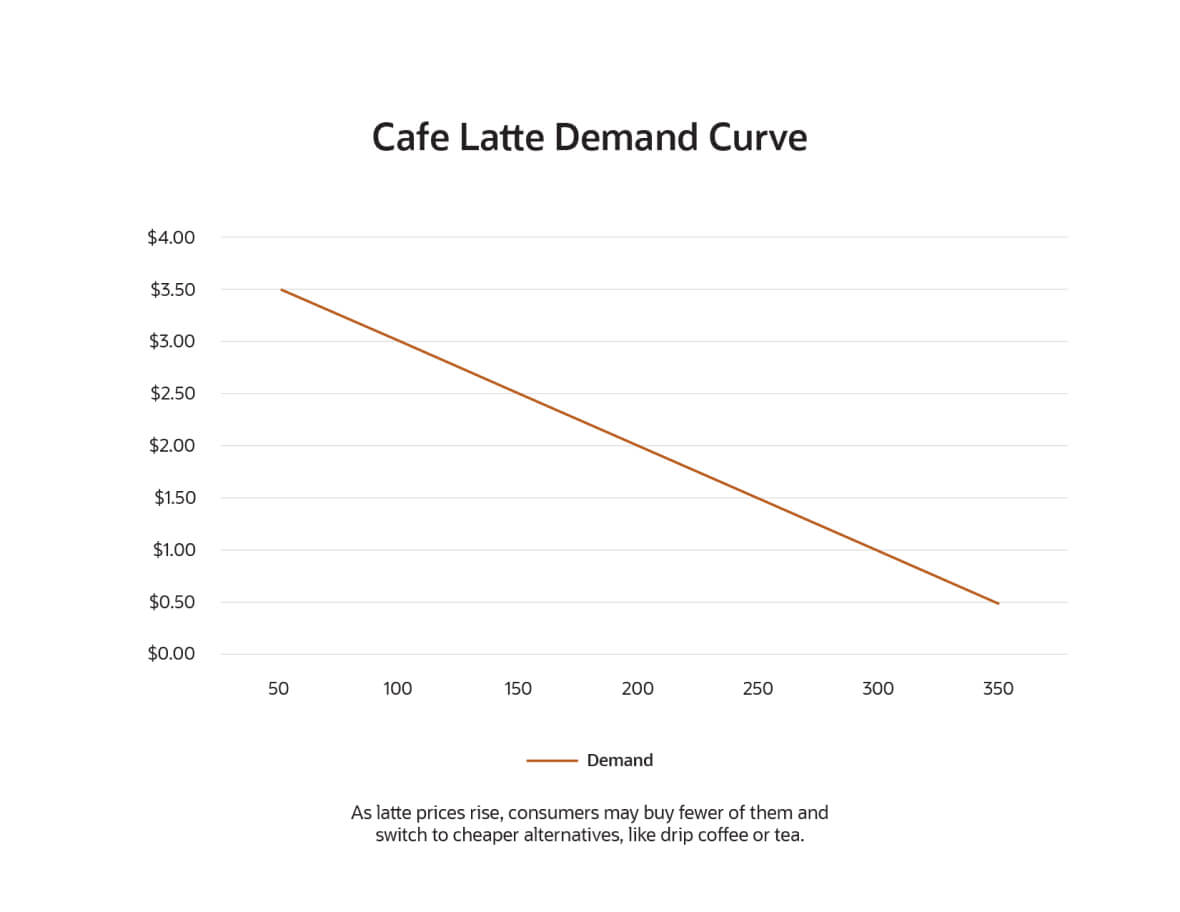
A demand curve is a graph that tracks the relationship between price (vertical axis) and demand (horizontal axis). The downward slope indicates that when prices rise, demand tends to fall.
The extent to which price changes affect demand varies from product to product. For any product, the steepness of the curve is a measure of its demand elasticity — the extent to which demand is affected by changes in the price. A less steep curve indicates that a small change in price causes a large change in demand.
Note that the demand curve only considers the effect on demand of a single factor — price. Other factors that influence demand, such as advertising, can shift the entire demand curve to the left or right.
Supply Curve
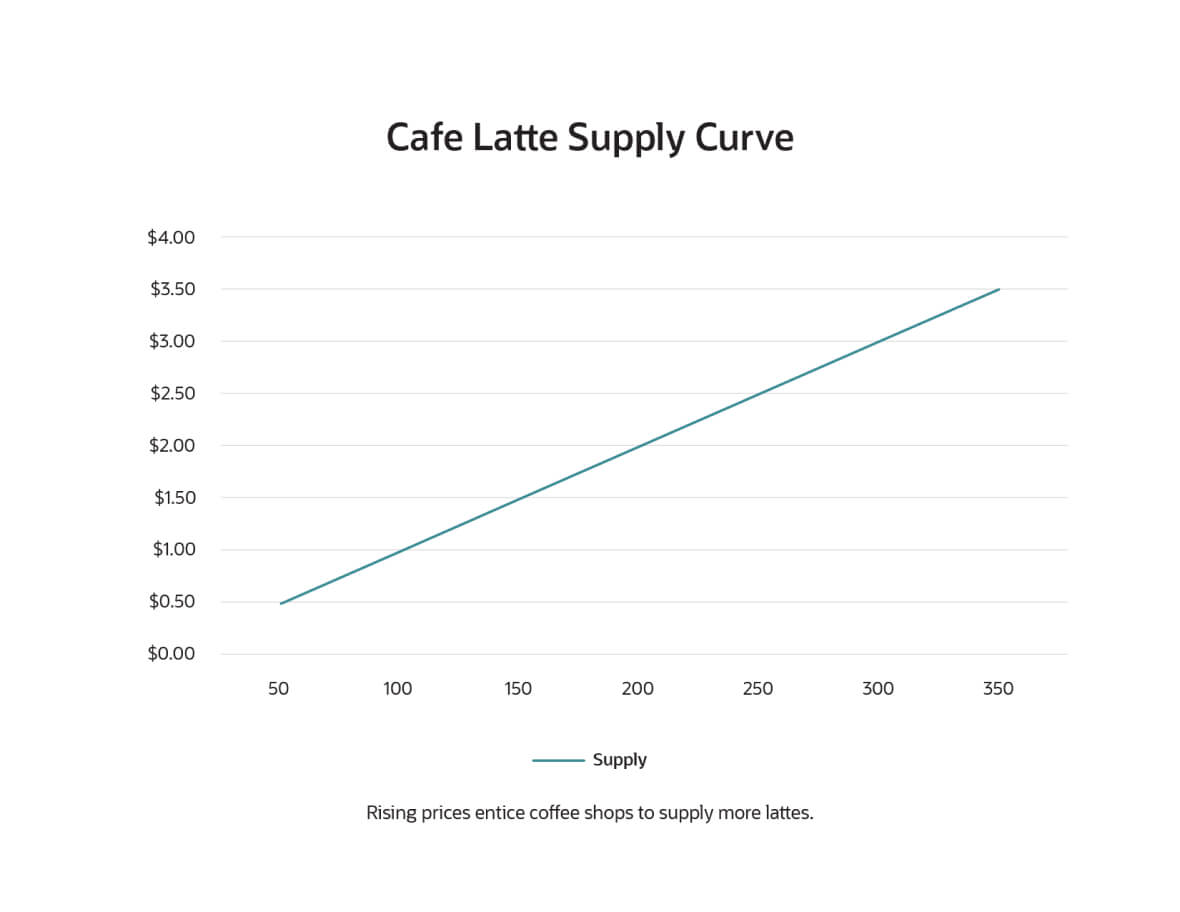
A supply curve shows the relationship between price (vertical axis) and supply (horizontal axis). It indicates how much output suppliers are willing to produce at different prices. When a supplier sees more profit potential from higher prices, it often will allocate more of its resources toward those more profitable items — usually at the expense of lower-priced items. At the same time, newcomers may enter the market, further increasing the available supply — because with the promise of higher revenue, more companies may be prepared to invest the startup costs required to enter that market.
Like demand curves, supply curves consider the effect of pricing but assume that everything else remains constant. However, other factors, such as production costs, can affect the supply. For example, if rising hamburger prices are dictated by more expensive beef, a restaurant owner may not see enough profit from the higher prices and may not have much incentive to expand capacity by adding another grill to the kitchen. Other constraints, such as limits on manufacturing capacity or the availability of raw materials, may also negatively impact the ability to increase supply.
Balance Between Supply and Demand
Understanding the balance between supply and demand is critical in many industries. Price is a key factor in determining this balance — although it's not the only factor. The extent to which price affects demand depends on the type of product being sold. It also depends on the competitiveness of the market. For some nonessential goods or items with many available substitutes, there will be high demand elasticity — and demand for one of those products will be highly affected by price changes. In contrast, demand for essential goods, like gasoline or health care, is relatively inelastic: If someone needs gas to get to work, they will probably pay for it no matter the price, especially if they don't have other options, like public transit.
Many other factors can affect the balance between supply and demand, thus impacting pricing. For example, supply can be affected by the cost of raw materials, technology that increases productivity, transportation or other supply chain issues, and government regulations.
Law of Supply and Demand Examples
The interlocking relationship between supply and demand can be seen at all levels of the economy. Here are some current and historical examples:
- Sports nutrition company MusclePharm sought to grow its business rapidly to meet expanding demand, but challenges included poor inventory visibility and accounting software that lacked the scalability and scope required to meet the company's objectives. Implementing a highly flexible, scalable and integrated enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution helped MusclePharm achieve 35x revenue growth within just a few years.
- Responding to rising demand, Earth-Kind created the first all-natural indoor rodent repellent approved by the FDA. Streamlining business operations with an integrated ERP system helped the company maintain a 40% growth rate and increase the supply of its products to 20,000 retail locations.
- As sales of high-end digital camera models rose during the 1990s, camera manufacturers invested in technology to increase production and expand the available supply. However, the resulting oversupply resulted in excess inventory and plummeting prices. The demand for digital cameras continued to decline as consumers switched to alternative products — smartphones that included cameras that were adequate for many uses.
- Demand for hand sanitizer rose during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic. As prices rose, some companies that saw a drop in demand for their primary products, such as breweries, saw an opportunity. Because they had the capability to make alcohol-based hand sanitizer, they started doing so. This increased the market supply, helping to meet the growing demand.
Better Supply and Demand Planning With NetSuite
NetSuite Supply and Demand Planning helps businesses balance supply and demand to ensure that they can fulfil customer orders while minimising excess inventory. Part of an integrated suite of business applications, NetSuite Supply and Demand Planning helps increase forecast accuracy, improve product availability, minimise inventory carrying costs and reduce production delays. NetSuite Demand Planning predicts inventory needs, based on factors such as historical demand, seasonality, growth and profit opportunities and sales forecasts. NetSuite Supply Planning helps companies determine how best to meet that demand, generating production and purchasing schedules and creating the relevant work orders and purchase orders.
Conclusion
The law of supply and demand can provide a useful model for understanding and determining pricing. It can help determine an equilibrium price, where suppliers can meet demand without overstocking, and customers get everything they need at a price they can accept. However, supply, demand and pricing can also be influenced by factors that the law of supply and demand doesn't consider, such as production costs, supply chain problems and regulations.
#1 Cloud ERP
Software
Law of Supply and Demand FAQs
What are the four basic laws of supply and demand?
The four basic laws of supply and demand are:
- If supply increases and demand stays the same, prices will fall.
- If supply remains constant and demand decreases, prices will fall.
- If supply decreases and demand stays the same, prices will rise.
- If supply remains constant and demand increases, prices will rise.
What is supply and demand in simple terms?
Supply is the amount of a specific good or service that's available in the market. Demand is the amount of the good or service that customers want to buy. Supply and demand are both influenced by the price of goods and services.
What is an example of the law of supply and demand?
If the price of coffee rises too much, some customers may stop buying coffee and switch to tea. If the price is too low, the reverse could happen, causing coffee shops to run out of coffee and lose potential profits. An equilibrium price would balance supply and demand, enabling coffee shops to avoid overstocks or shortages. At the equilibrium price, coffee shops can maintain profitability while keeping customers satisfied.
What is the basic law of demand?
The law of demand states that as prices rise, customers will buy the product in fewer quantities. This is often because they switch to other goods as replacements.









